Learning Java starts with understanding three important terms: JVM, JRE, and JDK. If you are a complete beginner, these words may feel confusing, technical, and difficult to remember. But once you understand what they really mean, Java becomes much simpler and easier to learn.
In this detailed guide, you will learn everything about JVM explained in a simple way, what JRE does, and why JDK vs JRE matters for developers.
This blog is written in a friendly, beginner-oriented manner so anyone can understand—even without programming experience in Java Full Stack Developer courses.
If you are planning to build a career as a Java developer or join Java Full Stack Developer courses in Coimbatore, learning these fundamentals is the first step. So let’s begin!
1. Introduction:
Before writing your first Java program, you must know how Java works behind the scenes. Java is famous for its slogan:
“Write Once, Run Anywhere.”
This means that a Java program written on Windows can run on Linux, macOS, or even mobile devices.
How is this possible?
Because of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Understanding JVM, JRE, and JDK helps you:
- Know how Java code is executed
- Choose the correct software tools
- Fix errors easily during development
- Build strong basics for Java, advanced topics, and frameworks
If you want to become a Java or full-stack developer, especially in institutions that offer the Best Java Full Stack Developer courses training in Coimbatore, this knowledge is absolutely essential.
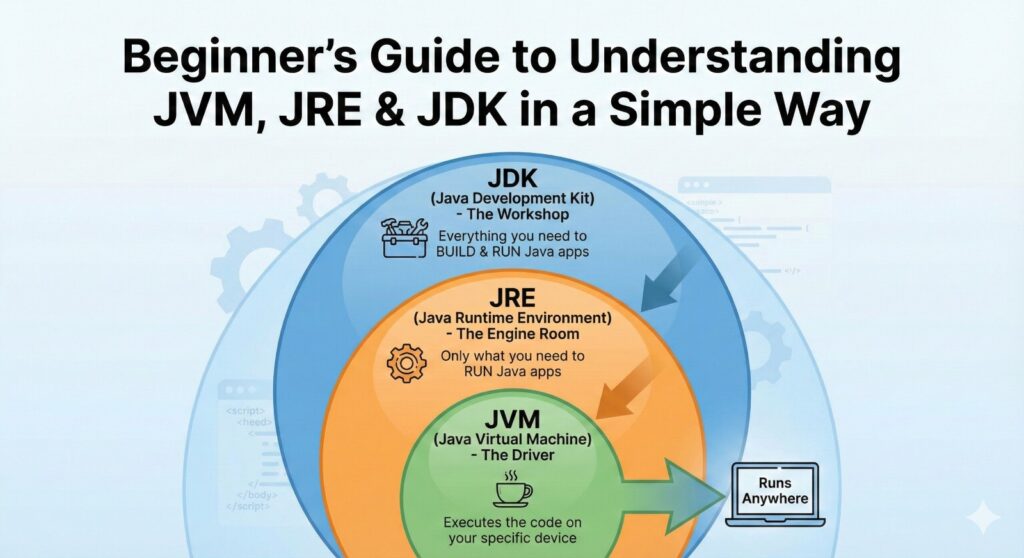
2. What is JVM?
2.1 JVM in Simple Words
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a special engine that runs Java programs. It does not understand Java code directly. Instead, it understands a format called bytecode.
Think of it like this:
If Java is the language you write, JVM is the interpreter that reads and executes it.
Key Responsibilities of JVM
Here are the important things JVM does:
- Reads and executes bytecode
- Allocates memory for variables, objects, and methods
- Performs garbage collection (automatically removes unused data)
- Handles security checks
- Ensures your program runs smoothly across different operating systems
Why JVM Makes Java Unique
JVM allows Java to run on any device because each OS has its own JVM.
You write code once, but JVM adapts it for each platform.
For example:
- JVM for Windows
- JVM for macOS
- JVM for Linux
All run the same bytecode without any changes.
That’s why Java is platform-independent.
3. What is JRE?
3.1 JRE in Simple Words
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is the package required to run Java applications.
If you only want to run a Java program (not write or compile), you just need the JRE.
It includes:
- JVM
- Core Java class libraries
- Supporting files
But it does not include tools for programming.
When Do You Need JRE?
- When you download a Java-based software
- When you want to run a Java desktop application
- When your computer needs Java for a specific tool
Today, many modern applications include their own runtime, but JRE is still essential in many environments.
4. What is JDK?
4.1 JDK in Simple Words
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is the complete package for Java programmers.
It contains everything in JRE plus the tools required to write, compile, debug, and build Java applications.
What JDK Includes?
Here are the main components:
- JRE (runtime environment)
- Javac compiler – converts source code into bytecode
- Debugger (jdb)
- JAR tool – packages programs
- Documentation tool (javadoc)
If you are learning Java programming or practicing full-stack development, you must install JDK.
5. JDK vs JRE
Many beginners get confused between JDK and JRE, but the difference is actually very simple.
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is meant only for running Java applications. It contains the JVM and the essential libraries required for execution. If you want to simply run Java-based software or applications on your computer, JRE is enough.
On the other hand, the Java Development Kit (JDK) is designed for developers who want to write, compile, and build Java programs. It includes everything the JRE has, plus additional tools like the Java compiler (javac), debugger, and development utilities in Java Full Stack Developer courses.
In short, JRE allows you to run Java programs, while JDK allows you to create Java programs.
So if you are learning Java programming or practicing for backend development—especially if you are joining Java Full Stack Developer courses in Coimbatore—you must install the JDK, not just the JRE.
6. How Java Code Runs: The 3-Step Process
Even if you are a beginner, it’s important to know how Java code becomes a running program.
Step 1: Writing the Code
You write a Java file like:
class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello World”);
}
}
This is the source code (.java).
Step 2: Compilation
The JDK compiler converts it into bytecode (.class).
Bytecode is a universal language readable by any JVM.
Step 3: Execution
JVM reads the bytecode and runs the program on your OS.
This flow ensures Java’s platform independence.
7. JVM Architecture
This is an important section, so points are included.
The JVM has several internal components that manage different tasks.
7.1 Main Components of JVM
1. Class Loader
- Loads class files into memory
- Ensures classes are loaded only once
- Handles loading from different sources
2. Memory Areas
JVM divides memory into:
- Method Area
- Heap Area (objects stored here)
- Stack Area (method calls)
- PC registers
- Native method stack
3. Execution Engine
Executes bytecode through:
- Interpreter
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Compiler
The JIT compiler converts repeated bytecode into machine code for faster execution.
4. Garbage Collector
Automatically removes unused objects to free memory.
5. Native Interface
Connects Java with native applications written in C/C++.
8. Why New Learners Often Mix Up JVM, JRE & JDK
Many beginners find JVM, JRE, and JDK confusing because the names sound similar and all three are closely connected in the Java ecosystem. Even though they work together, each one has a separate purpose. A simple way to understand them is this: the JDK includes everything needed to develop Java programs, the JRE provides the environment required to run Java applications, and the JVM is the virtual machine responsible for executing the bytecode. When you remember that JDK = JRE + development tools, JRE = JVM + libraries, and JVM = the engine that runs the program, the entire structure becomes much easier to understand. This simple formula helps beginners avoid confusion and gives them a clear picture of how Java works internally.
9. Which Version Should You Download? Advice for New Learners
Choosing the right JDK version is another area where many beginners hesitate. At the moment, the most widely used versions across companies are JDK 8, JDK 11, and the newer long-term support editions like JDK 17 and JDK 21. While JDK 8 still powers many legacy systems, most modern developers and companies prefer JDK 11 and JDK 17 for their stability and updated features. For students or those joining Java Full Stack Developer courses in Coimbatore, JDK 17 is often the best choice. Java Full Stack Developer courses, It offers modern capabilities, smooth performance, and compatibility with today’s popular frameworks. Since many organizations have already switched to JDK 17 for production use, learning with this version gives beginners an advantage in both understanding and employability.
10. Frequent Beginner Mistakes and How to Prevent Them
It’s completely normal for beginners to make mistakes when they first start working with Java. One of the most common errors is installing only the JRE, which is not enough for writing programs. To compile and develop Java applications, the JDK is essential Java Full Stack Developer courses. Another issue frequently seen is incorrect PATH configuration. If the system doesn’t recognize commands like javac, it usually means the PATH variable was not set properly. Many learners also confuse the role of the JVM and JRE, assuming they are the same. However, the JVM handles execution, whereas the JRE provides the necessary environment and libraries. Some beginners install multiple JDK versions without understanding the differences, which can cause unnecessary confusion during development. Another misconception is believing that the JDK is meant only for advanced programmers, when in reality, even the simplest Java programs require it. Avoiding these mistakes can make the learning process much smoother and more enjoyable.
11. How JVM, JRE & JDK Knowledge Strengthens Your Full Stack Development Skills
For aspiring full stack developers, understanding how JVM, JRE, and JDK work is not optional—it’s essential. As a backend developer working with Java, you will deal with servers like Tomcat, Spring Boot, or JBoss, all of which rely on the JVM. You may need to deploy applications, analyze runtime errors, troubleshoot memory issues, or work with frameworks like Spring, Hibernate, and Servlet-based systems. Each of these technologies sits on top of the JVM. Students enrolled in the Best Java Full Stack Developer courses training in Coimbatore are always encouraged to build a strong understanding of these fundamentals before diving into advanced development. When you clearly understand how the JVM manages execution, memory, and performance, you become more confident in building scalable and reliable Java applications Java Full Stack Developer courses.
12. Real-World Scenario: How JVM Supports Enterprise Applications
Java remains the backbone of many large-scale applications because of the JVM’s stability, security, and performance. In industries such as banking, finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, Java-powered systems handle millions of user requests every day. The JVM ensures that these applications run smoothly by managing memory efficiently, optimizing performance, and supporting massive workloads without crashing. For example, a banking application built using Java can run seamlessly across different server environments because the JVM adjusts itself based on the hardware and operating system. This ability to deliver consistent performance across platforms is one of the main reasons enterprises trust Java for mission-critical applications.
Conclusion
By now, you should have a clear and beginner-friendly understanding of what the JVM, JRE, and JDK really are and why they matter. You’ve learned the difference between JDK vs JRE, how the JVM executes Java programs, how memory is organized behind the scenes, and why these concepts form the backbone of full stack development. Java Full Stack Developer courses Understanding these basics will help you learn Java faster, solve problems more effectively, and feel confident as you move deeper into real-world coding.
If you’re looking for structured guidance, practical training, and expert mentorship, Brainery Spot Technology offers one of the Best Java Full Stack Developer courses training in Coimbatore. Their approach makes complex topics like JVM, JRE, and JDK easy to understand, even for complete beginners. With hands-on practice, real-time projects, and personalized support, they help you build a strong foundation and grow into a skilled Java Full Stack Developer courses.
A strong base leads to a strong career—and with the right training at Brainery Spot Technology, you’ll be well-prepared to begin your journey in Java Full Stack Developer courses.
